Concerned about high energy bills but unsure where the heat is escaping?
Many property owners waste thousands on ineffective insulation upgrades because they don’t know their actual U-values.
Our U Value Calculator eliminates this guesswork by accurately measuring how much heat transfers through your building materials—helping you identify problem areas and make targeted improvements that actually reduce energy costs rather than spending on solutions that don’t address your specific heat loss issues.
Free Online U Value Calculator
Use our free online U Value Calculator to calculate the U value for your project.
Simply choose your units of choice, add in the layers you need, and calculate the u values.
U-Value Calculator
Heat Loss Estimation
A U-value (thermal transmittance) measures how effectively a material or building element (such as a wall, roof, window, or floor) allows heat to pass through it.
It is expressed in W/m²·K (watts per square meter per degree Kelvin), where lower values indicate better insulation and reduced heat loss. The U-value is calculated as the reciprocal of the total thermal resistance (R-value) of all layers in a construction assembly, including surface resistances. It is a crucial metric in building energy efficiency, as regulations and energy codes often set maximum allowable U-values to improve insulation and reduce heating and cooling costs.
In some regions, U-values may also be expressed in BTU/(hr·ft²·°F), the imperial equivalent.
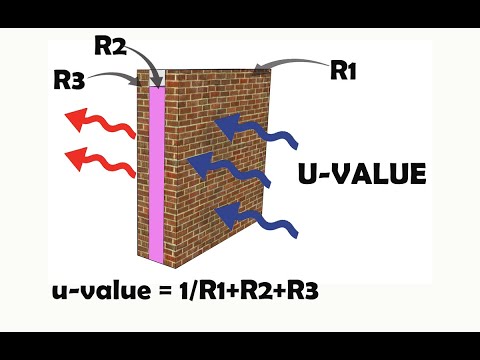
How are U Values Calculated?
A U-value tells us how much heat passes through a material or a combination of materials. The lower the U-value, the better the material is at keeping heat inside (or outside) a building.
To calculate the U-value, we first find the thermal resistance (R-value) of each layer in the structure. Thermal resistance depends on two things:
1. Thickness of the material (how thick it is, measured in meters).
2. Thermal conductivity (how easily heat moves through it, measured in W/m·K).
We calculate the R-value of each layer like this:
R = Thickness ÷ Thermal Conductivity
Once we have the R-values for all layers, we add them together to get the total resistance (R-total) of the structure.
Finally, the U-value is simply:
U = 1 ÷ R-total
The lower the U-value, the better the insulation!
More Useful Calculators
Looking for more handy tools? Check out our popular calculators to make your life easier:
✅ Meeting Cost Calculator – Find out how much time and money your meetings are really costing!
✅ Age Calculator – Instantly calculate your exact age in years, months, and days.
✅ BMI Calculator – Quickly check if you’re in a healthy weight range based on your height and weight.
Explore more free online calculators at Calculator Lord and simplify your calculations today! 🚀
Why do U Values matter?
Lower U-values mean better insulation, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in buildings.
What are the regulatory standards for U values?
Different countries have building regulations that set maximum allowable U-values for different components:
• Walls: ~ 0.18 - 0.35 W/m²·K
• Roofs: ~ 0.12 - 0.20 W/m²·K
• Windows: ~ 1.0 - 3.0 W/m²·K
Impact on Energy Efficiency
A low U-value reduces energy demand, making buildings warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
U Values for common materials
| Material | U-Value (W/m²·K) |
|---|---|
| Single Brick Wall (no insulation) | 2.00 |
| Cavity Wall with Insulation | 0.30 |
| Solid Concrete Wall (no insulation) | 2.20 |
| Timber Frame Wall with Insulation | 0.25 |
| Double Glazed Window | 2.70 |
| Triple Glazed Window | 0.80 |
| Flat Roof (uninsulated) | 4.50 |
| Flat Roof with Insulation | 0.18 |
| Pitched Roof with Insulation | 0.12 |
| Floor (concrete, no insulation) | 1.50 |
| Floor with Insulation | 0.20 |
U Value comparison for common building materials
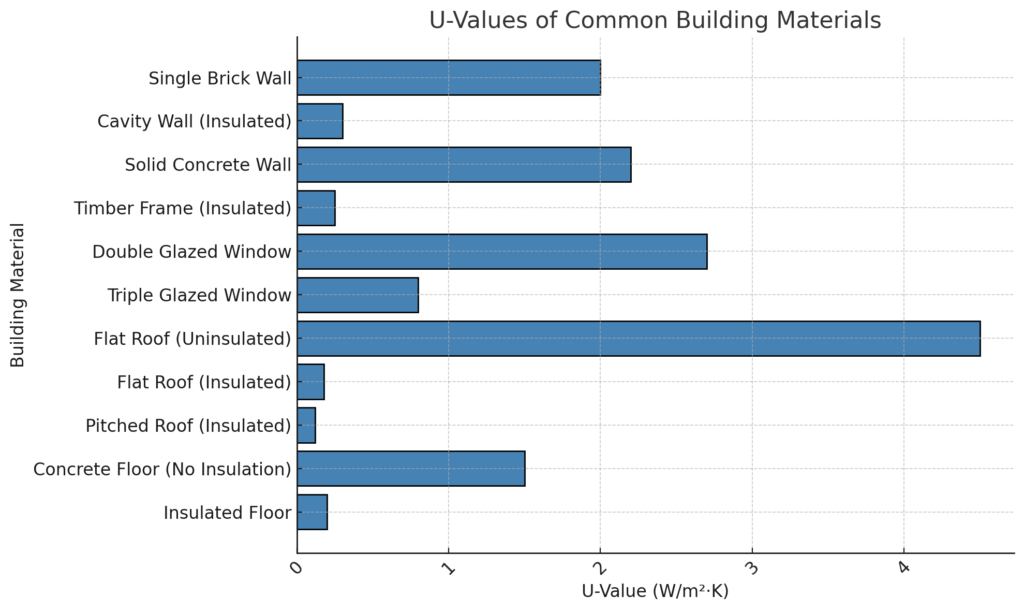
The above chart shows a comparison of the U values for common building materials.
As you can see, an uninsulated flat roof has a much higher U value than an insulated Flat Roof. This highlights the higher the U value, the worse the heat insulation value of the material.
Hopefully, you've been able to use our free online u value calculator to create a picture of how well insulated your project may be.
FAQ - Frequently asked questions about U-Values
What is a U-value?
A U-value measures how well a building part stops heat from passing through it. Lower U-values mean better insulation. The U-value tells us the rate of heat flow through a structure like a wall, roof, floor, or window. It counts all heat transfer types: conduction, convection, and radiation.
How do we measure U-values?
We measure U-values in Watts per square meter per Kelvin (W/m²K). This shows how many watts of heat energy pass through one square meter of material when the temperature differs by one Kelvin (or one degree Celsius) on each side. For example, a U-value of 1.5 W/m²K means 1.5 watts flow through each square meter when the temperature differs by 1 degree.
What U-values should I aim for in my home?
For good energy efficiency in new buildings, aim for these U-values:
Walls: 0.2-0.3 W/m²K or lower
Roofs: 0.1-0.2 W/m²K or lower
Floors: 0.2-0.3 W/m²K or lower
Windows: 1.2-1.6 W/m²K or lower
Building codes set minimum standards, but lower U-values will save more energy and money over time.
How can I improve the U-value of my walls?
You can improve wall U-values by adding insulation. For solid walls, add internal or external insulation boards. For cavity walls, fill the gap with insulation material. Thicker insulation gives better U-values. Other steps include using thermal breaks to stop heat bridges and making sure there are no gaps in the insulation
How do U-values affect my energy bills?
U-values directly affect your energy bills. A house with high U-values loses heat faster, so your heating system must work harder and use more energy. By improving U-values through better insulation, you can cut heating costs by 20-30%. Better U-values also mean more comfort, fewer cold spots, and less moisture build-up in your home.
Conclusion - U Value Calculator
U-Values are confusing. Using our U Value Calculator should hopefully simplify the process of calculating the energy efficiency of your home or workspace.
