Compound Interest Calculator: See How Your Money Grows Over Time
Finding it hard to stay motivated with your investment plan?
Without seeing the long-term impact of compound interest, many people abandon their savings strategy, missing out on thousands in potential wealth.
Our Compound Interest Calculator changes this by visually demonstrating how your money grows exponentially over time—turning the abstract concept of “interest on interest” into concrete numbers that keep you committed to your financial journey.
Compound Interest Calculator
Results
Final Account Balance:
Total Contributions:
Total Interest Earned:
Effective Annual Yield (Approx):
Real Rate of Return (After Inflation):
Yearly Breakdown
| Year | Starting Balance | Contributions | Interest Earned | Ending Balance |
|---|
Compound Interest Calculator: The magic of compounding
A Compound Interest Calculator shows how a starting deposit and recurring contributions build over time when interest adds to the principal on a regular schedule.
The compounding process is powerful because each interest payment combines with the principal, which boosts returns.
It gives investors, savers, and financial planners a simple way to see potential outcomes.
In addition, it works as a wealth growth calculator, financial planning tool, and investment calculator in one place.
How to Use the Compound Interest Calculator
Users enter a few simple details into this investment calculator:
- Initial investment (Principal amount)
- Annual interest rate (%)
- Compounding frequency (daily, monthly, quarterly, annually)
- Investment duration (years)
- Additional contributions (optional)
The interest rate calculator then processes these inputs and displays your total potential value. In addition, it acts as a savings calculator, future value calculator, and investment return calculator. You receive instant results on projected growth based on your preferred compounding schedule.
The Magic of Growth: Compound Interest Explained
What Is Compound Interest?
Compound interest adds periodic gains to your principal and then calculates new gains on that larger amount. This differs from simple interest, which calculates gains based on the original principal only.
Use this formula to see how it works:
A = P (1 + r/n)^(n*t)
Where:
- A = Final amount
- P = Initial principal
- r = Annual interest rate (in decimal form)
- n = Number of compounding periods per year
- t = Number of years
This compound growth model highlights how periodic interest adds momentum to your total balance. It reflects the time value of money, so each extra day or month can produce notable increases in your investment growth rate.
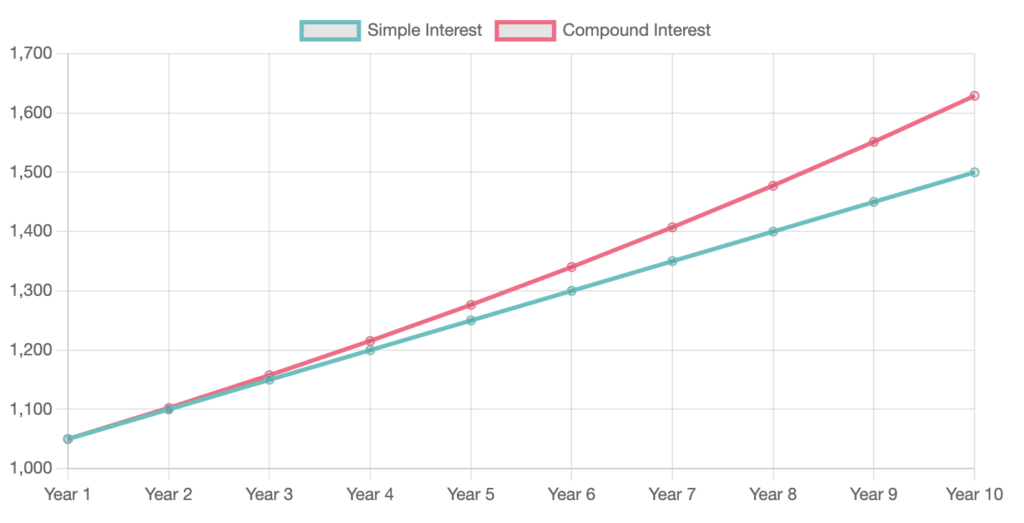
Visualising Compound vs Simple Interest
Here is a chart that shows the how compound vs simple interest diverge from the same initial invested amount
Now lets take a look at that same chart, but over 30 years
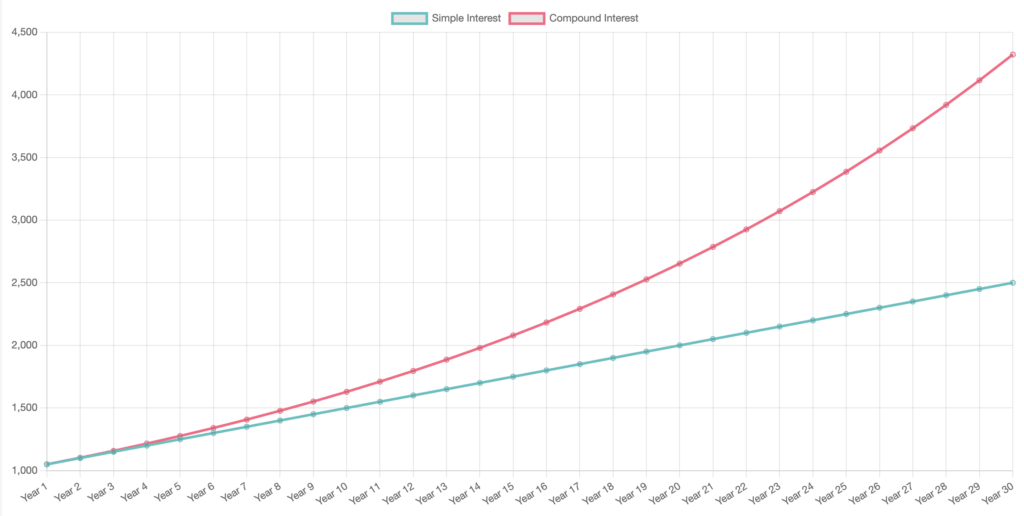
You can see that the longer the investment period, the larger the difference between simple and compound interest.
In our example here, from the same initial investment amount, the simple interest finishes at $2,500 and the compound interest account finishes at around $4,400 after 30 years.
If this doesn’t show you why compound interest is magic, I don’t know what will!
How Compounding Frequency Affects Growth

Compounding frequency is key to greater returns.
Daily compounding means interest adds to the balance each day, while monthly or quarterly compounding does so fewer times per year.
More frequent additions lead to faster gains.
For instance, a principal that compounds daily can overtake an amount that compounds annually, even if both share the same rate.
Some might prefer monthly interest accumulation, others prefer annual scheduling.
Each approach can shape the total outcome in this compounding frequency impact example. Over longer periods, high-frequency compounding often generates greater growth acceleration.
Check out some of other calculators
- Debt vs Investment Calculator – Compare the benefits of directing extra cash to debt repayments versus investing.
- Salary Sacrifice Calculator – Check how adjusting contributions from your paycheck might affect overall savings.
- Savings Calculator – View projected balances when adding regular deposits over time.
- ISA Calculator – See how a tax-advantaged account can potentially boost returns.
- AER Calculator – Check the annual equivalent rate for clearer insights on your interest gains.
- Percentage Calculator – Quickly review percentage changes and differences for everyday math.
Real-Life Examples of Compound Interest in Action
- Savings Account Growth
- Start with $1,000 in a savings account at 5% for 10 years.
- Daily or monthly compounding leads to a balance that goes beyond simple interest results.
- This is a good demonstration of a retirement savings calculator in a simpler context.
- Stock Market Investment
- Invest $10,000 in an index fund for 20 years.
- Dividends and reinvested earnings boost overall investment compounding.
- A mutual fund calculator approach might show how reinvestments add to the final amount.
- Retirement Planning
- Steady deposits into a retirement plan can multiply gains.
- A 401(k) growth scenario reveals how smaller contributions compound significantly over time.
The Power of Starting Early – Why Time Matters
Time can transform a small investment into a substantial account balance. For example:
- Investor A deposits $100 per month, starting at age 25.
- Investor B deposits $200 per month, beginning at age 40.
Even though Investor B deposits more per month, Investor A often finishes with a higher balance. A visual chart of long-term financial growth shows the impact of an extended investment horizon. This is a prime factor behind major wealth accumulation.
Types of Investments That Benefit from Compound Interest
Stock Market & Mutual Funds
Many equities distribute dividends. When those dividends are reinvested, your principal grows further. Over the years, an index fund growth approach with a dividend reinvestment plan (DRIP) can deliver significant increases. A stock market return calculator helps illustrate these outcomes for various funds.
High-Yield Savings Accounts & CDs
Banks often offer higher rates in special savings or CD accounts. A high-yield savings calculator reveals how the balance can surpass returns from a standard account. A CD rate comparison indicates how depositing funds for fixed durations can lead to additional interest gains.
Retirement Accounts (401k, IRA, Roth IRA)
Tax-advantaged accounts such as 401(k) or IRAs can multiply the benefits of compound interest. Regular contributions plus any employer matches can boost balances over the long term. A 401(k) growth calculator or IRA investment planner is helpful for seeing how a steady retirement portfolio calculator approach can shape a stable future.
FAQs About Compound Interest & Our Calculator
How Does Compounding Work in Real Life?
Compounding appears in savings accounts, stock investments, and loan balances. Positive compounding produces higher returns, while negative compounding in debt adds extra costs.
Is Compound Interest Better Than Simple Interest?
Yes. Simple interest only applies to the original principal. Compound interest grows the principal with each earned amount.
What’s the Best Way to Make the Most of Compound Interest?
Start early, invest frequently, select high compounding intervals, and reinvest all gains.
Can I Use This Calculator for Loan Interest?
Yes. Loans often rely on compound interest in reverse. You can also check a loan-focused tool to explore potential costs more precisely.
Conclusion
A Compound Interest Calculator helps you see how small steps can lead to strong growth over time. It shows the effects of regular contributions, varied compounding schedules, and realistic interest rates. In short, compounding can turn modest amounts into a meaningful sum. By using this tool, you can explore different scenarios and find a path that suits your financial goals. Above all, a careful approach with consistent deposits can produce significant results, particularly when you start early.
